The evolution of mobile communication standards is advancing to the next level with the emergence of 5G technology, which aims to connect devices, machines, businesses, and people. While 5G technology has been deployed in some developed markets over the past two years. The focus is now shifting toward “5G-Advanced” (3GPP Release 18), which introduces enhanced AI and machine learning capabilities to the network.
Although the initial rollout of 5G is primarily focused on traditional mobile applications, its unique combination of ultra-low latency, carrier-class reliability, high scalability, and ubiquitous coverage has the potential to revolutionize innovation across multiple vertical industries. With global 5G connections projected to exceed 3 billion by 2026, we are entering an era of “intelligent connectivity.” This blog explores the current trends, challenges, and future opportunities of 5G Networks.
5G Networks: Next Generation of Mobile Communication
5G network technology aims to deliver faster data speeds, lower latency, higher reliability, and greater network capacity than previous generations. Unlike 4G, which was primarily a “mobile-first” generation, 5G is “software-defined,” leveraging Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to create flexible, virtualized slices of the network tailored to specific needs.
The emergence of 5G scope can transform various industries by enabling new levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation through seamless connectivity between devices. To support this innovation, Tessolve, with its extensive technical expertise in wireless and wired markets, provides 5G testing services.
Tessolve’s solutions and services can assist in the development of 5G technology and help bring finished products to market sooner, thus supporting the transformative potential of 5G.
Spectrum: The Multi-Layer Strategy
A key innovation in 5G is the use of a “layered” spectrum approach to balance coverage and speed:
- Low-Band (Below 1 GHz): Wide coverage and deep indoor penetration; ideal for nationwide reach.
- Mid-Band (1 GHz – 7 GHz): The “sweet spot” for 5G, providing a balance of coverage and speeds up to 1 Gbps.
- High-Band (mmWave, 24 GHz+): Delivers ultra-high speeds (up to 10 Gbps) but has a short range; used in stadiums and urban hotspots.
Challenges Associated With the 5G Networks
The implementation of 5G networks also presents several challenges that must be addressed. Here are some of the key challenges with the 5G networks:
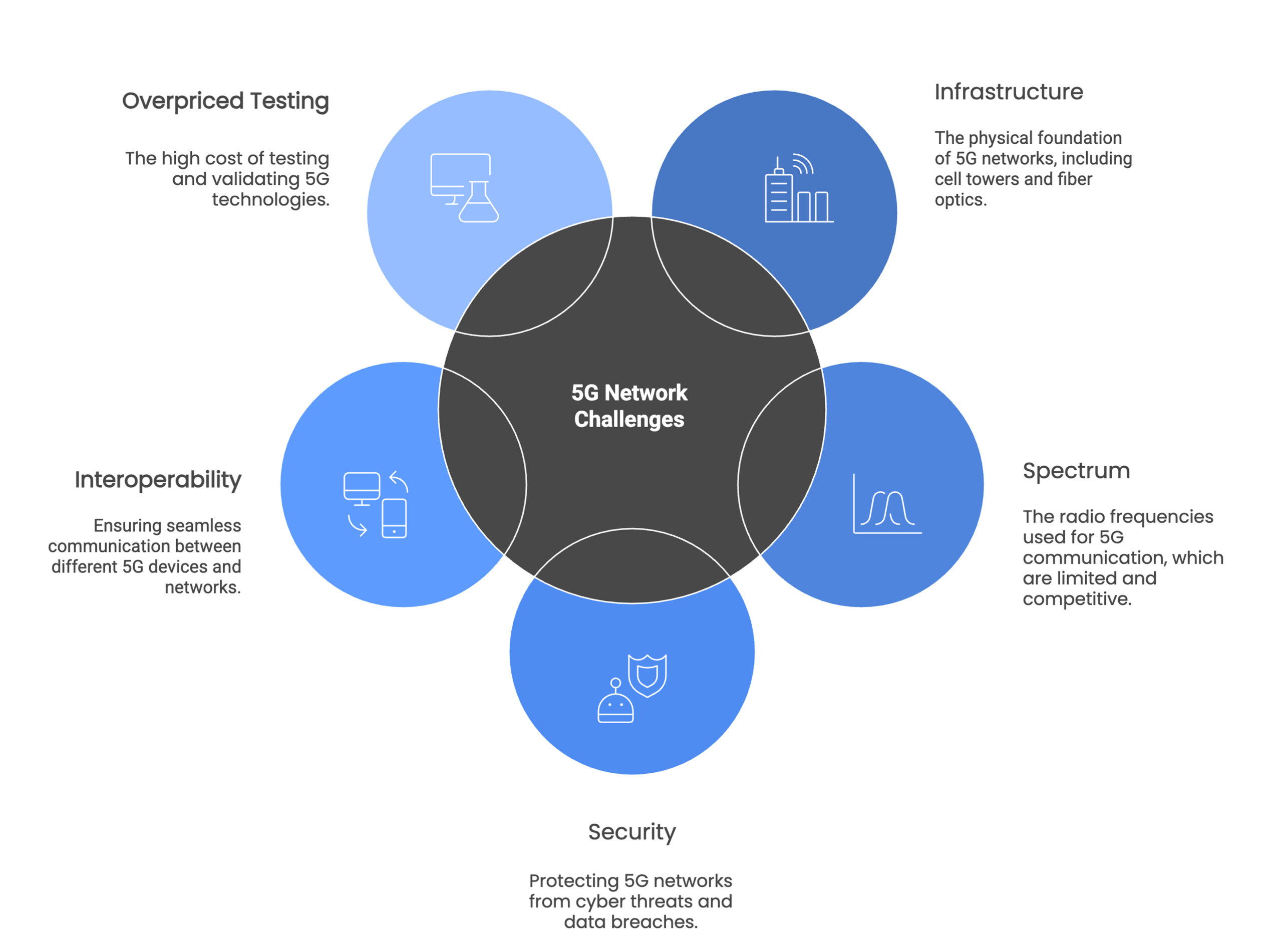
- Infrastructure:
It requires a significant amount of new infrastructure, including additional cell towers, fiber optic cables and other related equipments. Building this infrastructure newly can be expensive and time-consuming. - Spectrum:
It requires a significant amount of new spectrum to operate effectively. However, finding and allocating new spectrum can be challenging, especially in urban areas with high demand for spectrum. - Security:
It may be more vulnerable to cyber threats than previous generations due to its increased complexity and use of new technologies. This makes security a critical challenge that must be addressed. - Interoperability and Open RAN:
5G needs to be interoperable with existing networks. The emergence of Open RAN (Radio Access Network) is a major trend, allowing operators to mix and match hardware and software from different vendors, breaking the traditional vendor lock-in.
- Overpriced testing:
Overpriced 5G testing can hinder innovation, limit competition and compromise the quality and safety of 5G technology. It is, therefore, important for testing services to be priced fairly and competitively to support the growth and development of the 5G industry. However, tessolve’s wireless testing services utilize a cost-effective process to identify issues within a specified timeframe. Tessolve is a reliable partner in providing on-time support and high-quality services, a key strength of our global business.

Unlocking Possibilities: The Power of 5G
The scope of 5G is best understood by scrutinizing the main usage models targeted by this megatrend namely enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communications(URLLC), and massive machine type communications (mMTC).
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
This use case addresses the user-centric applications for wireless access to multimedia content, services, and data. The demand for mobile broadband services has continuously increased in the past decade, leading the industry to significantly enhance the mobile broadband capabilities.
Typical eMBB applications
- UHD video (4K, 8K) 3D video
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Tactile Internet, Cloud gaming, and Broadband kiosks
- Real-time simulation and training
- Remote classroom, Hologram
Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC)
This use case is characterized by a very large number of connected devices (e.g., a sensor network) typically transmitting relatively small payloads containing non-delay-sensitive data. These devices are required to be low cost and consume very low power.
Typical mMTC applications
- Smart Home
- Smart City
Why Tessolve?
At Tessolve, our testing services are designed to identify issues through a low-cost process within a specified timeframe, which can help improve the product’s quality and accelerate its release to market.
We are known for our reliability and commitment to providing excellent customer service. As a trusted partner, Tessolve can help businesses navigate the complexities of 5G testing and provide the support needed to bring their products to market successfully.
Overall, Tessolve’s expertise, cost-effective testing solutions, and commitment to customer satisfaction make it a compelling choice for businesses looking to develop and test 5G products.
What Are the Challenges of Signal Integrity in High-Speed PCB Design?
Conclusion
In conclusion, 5G networks have the potential to revolutionize the way we live, work, and communicate. The high-speed and low-latency capabilities of 5G technology will enable innovative new applications and services, creating new business opportunities across various sectors. However, future of 5G technology also comes with significant challenges, including cost, infrastructure, and security concerns.
FAQs
1. What is “5G-Advanced”?
It is the next phase of 5G (Release 18) that uses AI to make networks more energy-efficient and improve connectivity for high-speed trains and drones.
2. How does 5G differ from 4G in architecture?
4G is hardware-centric, while 5G is “Cloud-Native,” meaning network functions run as software on standard servers, allowing for “Network Slicing.”
3. What is Open RAN?
Open RAN allows mobile operators to use equipment from multiple vendors on one network by using standardized, open interfaces.
4. How do 5G and future networks enable new technologies?
By providing the “Digital Fabric” ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, necessary for real-time AI processing, remote surgery, and fully autonomous transportation.