Scaling production from prototype to millions of units is one of the toughest challenges in modern engineering. Speed, cost, and innovation often dominate the conversation, but without robust processes, quality can quickly erode at high volumes. High-volume test engineering bridges this gap, ensuring that products perform reliably while keeping pace with manufacturing demands. From early design considerations to advanced automation and analytics, organizations must adopt structured practices to safeguard quality at scale. This blog explores the best practices in high-volume test engineering that help companies deliver consistency, reliability, and trust, no matter the production size.
The Importance of High-Volume Test Engineering
High-volume test engineering ensures that every unit leaving the production line meets strict quality and performance standards. In industries like automotive, consumer electronics, and semiconductors, a single defect can lead to massive recalls, reputational damage, and financial losses. Effective test strategies minimize these risks by:
- Detecting defects early in the production cycle.
- Reducing time-to-market through automated workflows.
- Improving yield while lowering per-unit test costs.
- Creating scalable systems that evolve with product complexity.
With this foundation, let’s explore the best practices in high-volume test engineering that enable organizations to deliver quality at scale.
AI in Test Engineering: Use Cases, Tools, and Real-World Impact
Best Practices in High-Volume Test Engineering
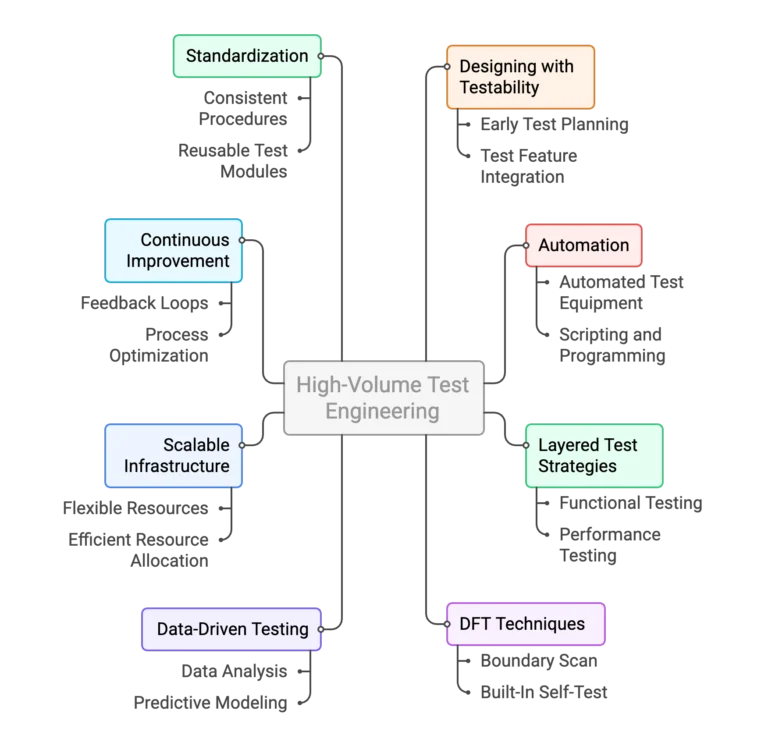
1. Designing with Testability in Mind
The path to reliable testing starts during the design phase, not on the production floor. Embedding test hooks, ensuring signal observability, and adding diagnostic features make downstream testing more predictable. Early adoption of strong test engineering practices ensures faster debug cycles and improves quality engineering outcomes, reducing costly late-stage issues.
2. Embracing Automation in High-Volume Test
Manual inspection cannot keep pace with the demands of high-volume production. Automated test equipment (ATE) systems, regression pipelines, and digital test scripts minimize human error while ensuring repeatable results. Automation also enables continuous regression against golden samples, a cornerstone for scalable semiconductor testing.
By capturing detailed logs and statistical data, automated workflows accelerate root cause analysis, enabling quicker corrective actions.
3. Layered Test Strategies for Broader Coverage
A robust test plan relies on diversity. Combining wafer sort, burn-in, final test, system-level validation, and field telemetry provides a safety net for catching different failure modes.
- Parametric testing ensures compliance with electrical specifications.
- Structural testing identifies process related defects and failures.
- Functional testing validates system-level features.
- Stress and aging tests highlight early-life failures emphasizing product reliability.
This layered approach, managed by expert test engineering teams, reinforces quality engineering metrics and reduces field escapes.
4. Leveraging Design-for-Test (DFT) Techniques
Design-for-Test (DFT) and Design-for-Yield (DFY) are essential enablers in scaling production. Embedding built-in self-test (BIST) structures, scan chains, and observability nets helps reduce test time and improve defect localization. DFT-driven semiconductor testing makes high-volume testing cost-effective without compromising coverage, while also accelerating time-to-market.
5. Data-Driven Testing and Analytics
Data is central to modern test engineering. By aggregating per-device telemetry into analytics dashboards, teams can monitor yield, variance, and process drift in real time.
Key practices include:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Cpk/Ppk trend tracking
- Pareto analyses for root cause identification
When quality engineering and test engineering teams share a single source of truth, response times improve and decision-making becomes more proactive.
6. Building Scalable Infrastructure
Scalable lab infrastructure is essential for handling large volumes. Modular test floors, parallel test cells, and standardized fixtures allow for flexible expansion. Modern facilities increasingly adopt digital twins to validate ATE programs before deployment, improving test engineering efficiency.
Investing in product reliability and qualification labs ensures that devices are stress-tested under real-world conditions, feeding valuable insights back into both design and quality engineering.
7. Embedding Continuous Improvement
High-volume success requires more than equipment; it requires culture. Training engineers in failure analysis, creating standardized escalation paths, and maintaining knowledge repositories ensures lessons are not lost. Cross-functional collaboration between design, product, test and failure analysis fosters continuous improvement in semiconductor testing workflows.
8. Standardization and Reusability
Reusable ATE libraries, standardized vectors, and hardware abstraction layers reduce overhead across projects. Such platform-agnostic approaches enable faster test development and smoother migration between vendors. This not only strengthens test engineering agility but also improves cost efficiency for high-volume semiconductor testing.
9. Collaborating Across the Ecosystem
Collaboration with suppliers and subcontractors is vital. Aligning on quality agreements, sharing datasets, and maintaining closed-loop feedback from field returns ensures systemic improvement. This ecosystem-level approach reinforces quality engineering at every stage of the product lifecycle.
The Role of Reliability in High-Volume Production
Reliability comprises more than just passing tests; it involves guarantees that products perform consistently in real-world conditions. Defects-per-thousands-of-parts-cost-issues, even small, can make thousands of defective products reach customers when production is scaled up. Reliability evaluation or stress, thermal, and environmental testing bolsters the paradigm. Weakness identification facilitates early prevention of expensive recalls and better customer confidence. Reliability practices also have feedback loops, thus enabling the team to achieve continuous improvement. Therefore, the integration of reliability testing into mass production in mission critical industries like Automotive, healthcare, aerospace, defense, etc. makes quality assurance a long-term performance instead of being a mere checkpoint.
Tessolve: Partnering for High-Volume Test Success
At Tessolve, we provide comprehensive solutions that help customers deliver quality at scale through state-of-the-art semiconductor testing, test engineering, and quality engineering practices. With more than two decades of expertise, we support chip design, post-silicon validation, ATE development, and system-level testing under one roof.
Our advanced Test Lab and Product Reliability & Qualification Lab are built for scalability, offering wafer sort, burn-in, and final test services backed by automation-driven workflows. Combined with advanced failure analysis and reliability solutions, we empower organizations to reduce time-to-market and improve yields.
As a trusted global partner, Tessolve helps companies optimize costs, accelerate ramp-up, and confidently scale production without compromising on reliability or performance. Explore our services to see how Tessolve can be your partner in achieving high-volume test success.