An embedded system is also termed an integrated system. It is a computer system designed by an embedded engineer to facilitate special functions, and its parts are mounted together onto a motherboard. A microcontroller or a microprocessor that consists of input and output interfaces and a small memory carries out the system’s central processing.
The programming language of the microprocessor or microcontroller, such as C, C++, Linux, and C#, can be used directly to program the systems. Real-time computing tasks can be carried out by designing embedded systems.
Modern embedded systems are increasingly tasked with Edge Computing, processing data locally to minimize latency and bandwidth dependence on the cloud. Specific use cases can be achieved using Tessolve MAGIK-II SOM+CB combination based on various SoCs, i.e., NXP, Qualcomm, TI, Renesas, etc., dedicated to developing and designing prototypes and applications with embedded systems.
Let us dive into detail about the concepts related to designing embedded systems.
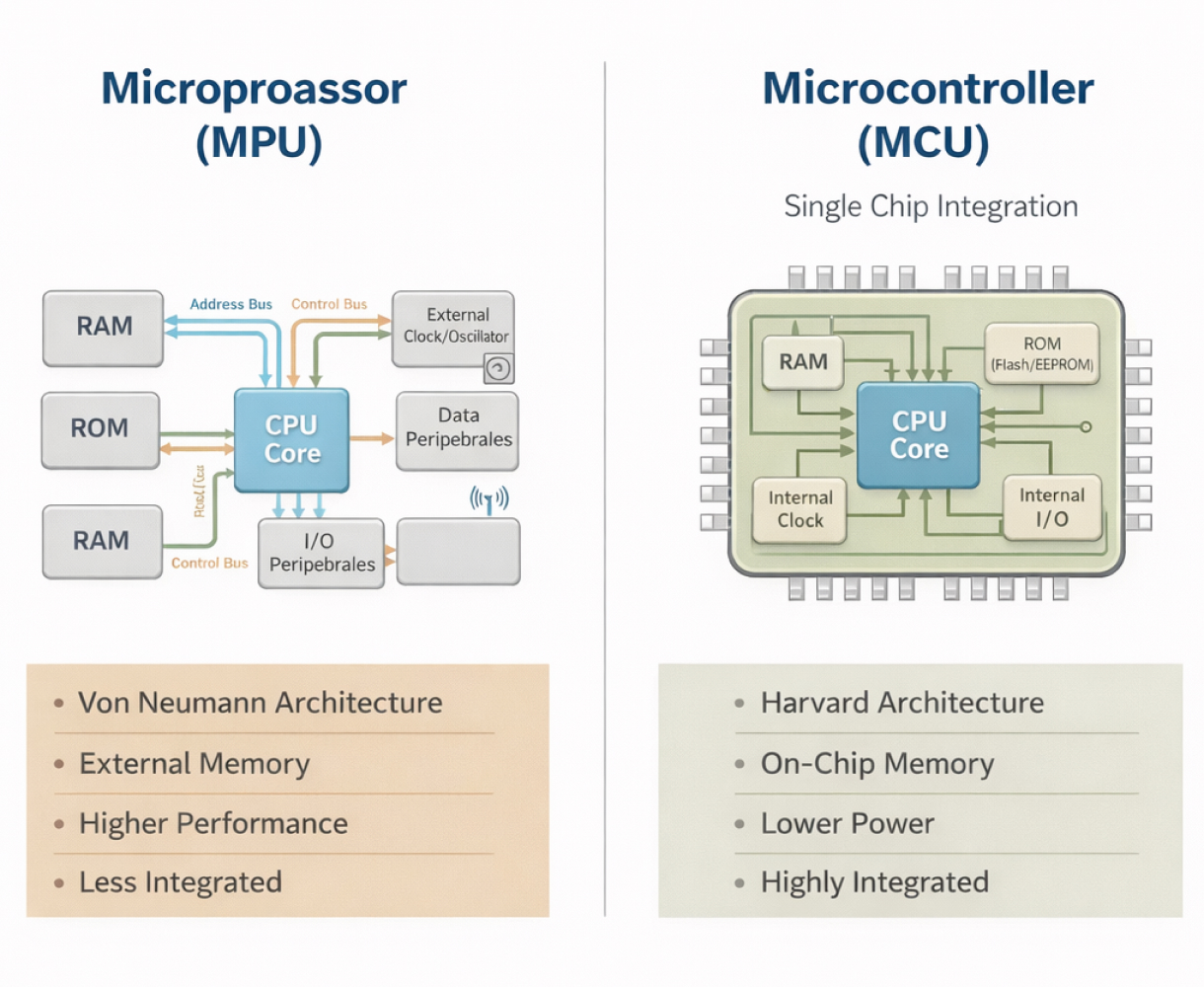
What Is a Microprocessor Unit?
The processor initially consisted of separate components interlinked through buses. For instance, the oscillator and the registers that signal the clock are all individual components. With the development in integration and technology, the various parts were coming together within the same circuit. Therefore, the earlier processors used to have multiple interconnected integrated circuits, and eventually, all the components came to be incorporated within a single circuit, known as a microprocessor.
The microprocessor is a part of the central processing unit (CPU). The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is present within the microprocessor and performs all the mathematical operations. The registers save the data for the moment, and the control unit harmonizes the working of the rest of the parts, that is, a ROM memory in which instructions are stored and other components.
Microprocessors are not used individually but are integrated with other systems for a particular function. Modern microprocessors increasingly utilize multi-core architectures to handle parallel tasks efficiently, and instruction set architectures like RISC-V are gaining prominence due to their open-source, customizable nature.
What Is a Microcontroller Unit?
A microcontroller is a computer with limited functionality. They have a simple design with low speed and are small. Computers have a processor and RAM. A microcontroller is an individual chip in which RAM, ROM, a processor, and other components are mounted together to aid programmers. DAC and ADC converters are placed together in different formats.
Therefore, they are not designed to manage an extensive software infrastructure. Most of the time, microcontrollers are directly programmed despite an embedded operating system. Because of this finite capability, a wide array of microcontrollers is established by different elements based on their use. The versatility allows you to choose the microcontroller that suits the project’s requirements, and is the primary reason they are so favored in embedded systems.
Key features distinguishing modern MCUs include advanced low-power modes (critical for IoT devices), integrated security features (hardware cryptography), and a higher prevalence of 32-bit architectures (like ARM Cortex-M) over older 8-bit versions for increased processing power.
About Development Kit
A development kit is a hardware component that aids in programming and testing another hardware element, such as a microcontroller, FPGA, or microprocessor. Usually, they are boards with the element in question that you would like to use along with different additional elements that simplify prototyping and programming.
The primary purpose is to help engineers learn, who later need to work with microcontrollers and microprocessors. Tessolve MAGIK-II development kits are good platforms based on various MCUs, MPUs/SoCs, and FPGA, which can help set up a development environment quickly and get started directly on application development for learning and POC purpose.
MAGIK-II platforms and their purpose
Tessolve has its own SOM Module Family MAGIK-2 modules based on the SMARC/Q7 standard, containing a complete software suite including Device Drivers, BSP, and support for various OS, allowing effective productization. Our SOM & EVK solutions allow Customers to start their software development before manufacturing and help faster time to market. These SOMs (System on Modules) address the complexity of modern multi-layer PCB design by providing a tested, robust core processing block.
MAGIK-II SOM family is ready to use a platform based on well-known processors from NXP, Qualcomm, Mediatek, Texas Instruments, and Renesas with Linux/Android OS/RTOS support and can be used for learning and developing POCs for application development for use-cases:
- Industrial
- Avionics
- Automotive
- Medical
- Internet of Things
- AI/Machine Learning at the Edge
About FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Arrays)
The reconfigurable hardware development obtained one of the most significant advantages, namely FPGA. Testing and designing hardware components are a hectic and time-consuming process that involves a lot of costs. There was no way of confirming that it worked until printing a design on a plate, and the printing process required time and money.
FPGAs are the solution to this problem. They are hardware parts interlinked with each other in a configurable manner, allowing you to select the parts you need and link them without printing them on the hardware. Embedded engineers need to use a particular language for the design, namely Hardware Description Language (HDL). An implement offered by the producer of the FPGA transforms that language into closed or open connections in the internal parts of the FPGA. The hardware circuit would remain the same and would perform the same function as it had been printed.
It made the building and designing process more convenient and allowed every design modification to be examined quickly. FPGAs were previously used for designing and prototyping but not as a finished product, whereas now, some FPGAs are being incorporated into the final product.
What Is SoC?
SoC stands for system on a chip and consists of a set of components that were initially separate but have been later integrated into a single chip. A CPU can form SoCs and FPGAs, or ESP32, a microcontroller SoC. It is a broad term that incorporates any technology fused within a single chip or board.
The modern trend in SoC design is Heterogeneous Computing, where multiple different core types (e.g., ARM Cortex-A for OS, Cortex-R for Real-Time, Cortex-M for low-power tasks, and dedicated Neural Processing Units or NPUs) are integrated to maximize power efficiency and performance for diverse applications.
What Is DSP?
DSP stands for digital signal processor and is used to deal with digital signals. It has widespread usage in treating video, audio, and telecommunications, and most of the technology we use regularly contains DSPs.
While traditionally separate, many modern SoCs now integrate dedicated DSP co-processors to efficiently handle complex tasks like noise cancellation, audio compression, and radar processing, reducing the need for standalone DSP chips in many applications.
What Are Real-Time Systems?
Real-time systems can maintain exact time measurements that can be utilized in situations where the reaction time is crucial. The validity of results relies on whether the stipulated time limit has been met. These systems are categorized as Hard Real-Time (missing a deadline results in catastrophic failure, e.g., avionics) or Soft Real-Time (missing a deadline results in degraded performance, e.g., video streaming). All modern cars have control systems that are based on real-time systems.
Designing embedded systems is significant as they play an essential role in our daily lives. All technical devices require embedded systems to function correctly and provide limitless opportunities for every sector. Tessolve has expert embedded engineers who build designs that enhance the efficiency of the embedded systems using cutting-edge platforms like MAGIK-II to tackle challenges in security, power management, and real-time processing. For better assistance from our experienced engineers, email us today at sales@tessolve.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the primary difference between an MPU and an MCU?
An MPU relies on external memory (less integrated), while an MCU has all components, including memory, on a single chip (highly integrated).
- What is the biggest advantage of using an SoC in modern embedded systems?
SoCs enable Heterogeneous Computing, integrating multiple core types (CPU, NPU, DSP) onto one chip for specialized, highly efficient performance.
- How have FPGAs evolved in embedded system design?
They are now widely incorporated into final products, primarily for high-performance computing and custom hardware acceleration of AI/Deep Learning.
- What is the main characteristic that defines a Real-Time System?
The validity of the result relies strictly on meeting a stipulated time limit, categorized as either Hard (catastrophic failure) or Soft (degraded performance).